The term computer language is sometimes used interchangeably with computer programming languages. Like humans, a computer also needs a language to communicate with the user or the developer. These special-purpose languages are known as programming languages or Computer languages.
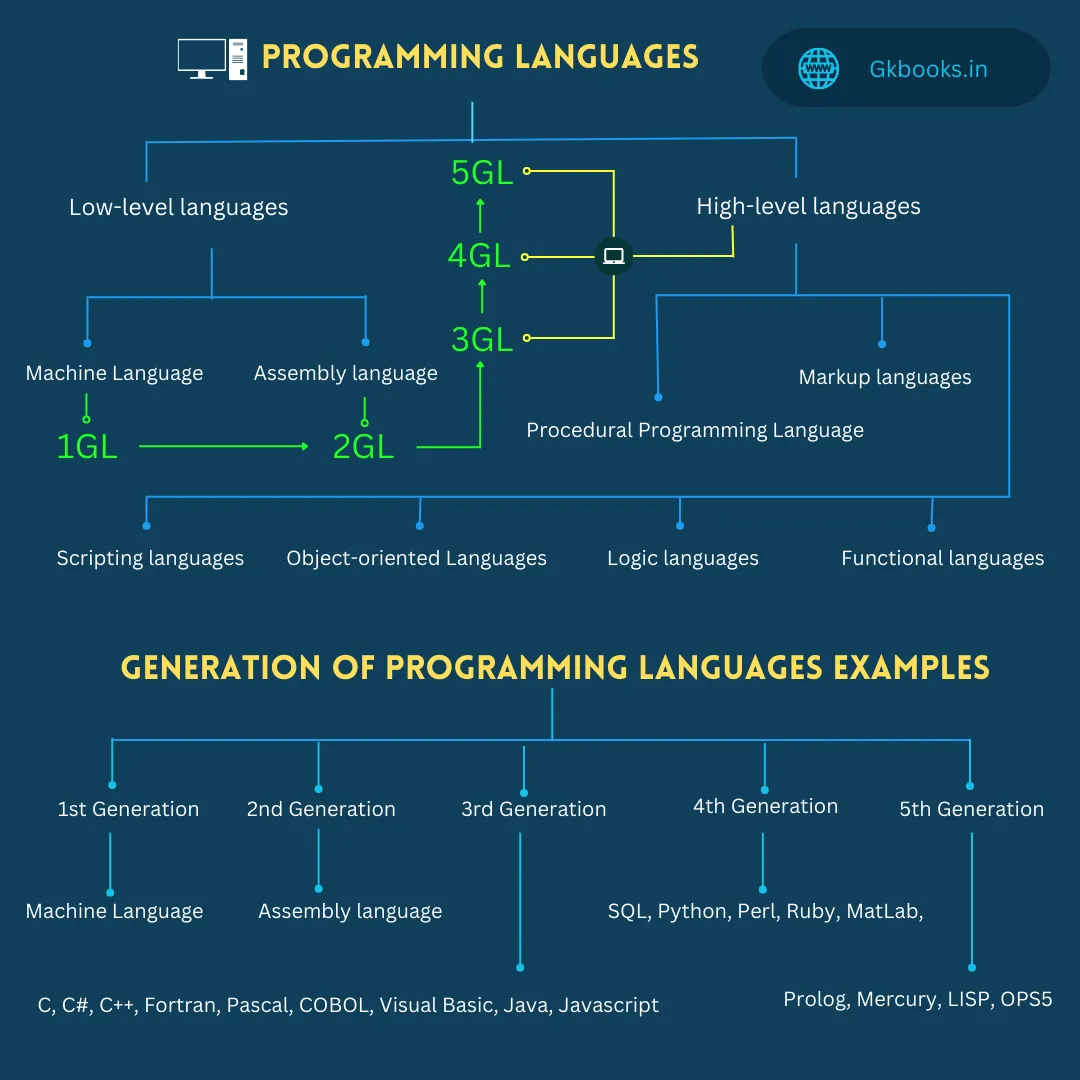
▪ There are different types of programming languages to perform specific tasks, those languages are divided into 5 generations based on function.
▪ Hard to find errors Since programs are written in a binary code consisting of 0’s and 1’s, it makes it difficult to find an error in their written code.
▪ Lack of portability: They are tied to specific hardware architectures and cannot be easily ported to other platforms without rewriting.
▪ Lack of abstraction and error-prone: It provides no high-level features, meaning programmers have to write low-level code to perform even simple tasks. This can be time-consuming and error-prone.
▪ Poor error handling: Built-in error handling or debugging features are missing in this generation of languages, which can make it difficult to identify and fix problems in a program.
▪ Lack of support for software engineering principles: Provide no support for software engineering principles, such as modular design and structured programming, which can make it difficult to write maintainable and reliable code.
▪ Poor support for large-scale development: They are not suitable for large-scale development projects, as they do not provide the necessary tools and abstractions to manage complexity.
Second-generation (2G) languages
▪ Second-generation languages are called low-level assembly languages.
▪ Assembly language has a human-readable notation that is more readable and easier to write than first-generation languages.
▪ It uses an assembler to interpret the instruction, which converts assembly-level instructions into machine-level instructions.
▪ Example of second-generation language: Assembly Language
Advantages of Second-generation languages
▪ Portable: Programs written in 2GLs can often run on a wide variety of computers and operating systems without requiring significant modifications, making them more portable than programs written in first-generation languages.
▪ More flexible: Provide a wide range of features and programming constructs, such as loops, arrays, and functions, which make writing complex programs easy.
▪ Easier to learn: Second-generation languages use more familiar, English-like syntax and are generally easier to read and understand than first-generation languages.
▪ More efficient: They are compiled or interpreted into machine code, making them more efficient to run than programs written in first-generation languages.
Disadvantages of Second-generation languages
▪ Slower than first-generation languages: 2GLs can sometimes be slower than programs written in 1GLs because 2GLs are compiled or interpreted into machine code while 1st-generation languages are executed directly by the computer’s hardware.
▪ More memory required: It requires more memory to run than those written in first-generation languages, as they may include additional instructions for the compiler or interpreter to execute.
▪ More complex than 1st Generation language: Second-generation languages offer a wider range of features and programming structures, which can make them more complex to learn and use.
Third-generation (3G) languages
▪ Third-generation or 3GL languages are high-level procedural languages and are more abstract and closer to human language.
▪ They are easier to write, read and maintain than 1G and 2G languages because the written instructions consist of a series of words like English.
▪ Examples of third-generation languages: C, C++, PASCAL, FORTRAN, COBOL, Visual Basic, and Java.
Advantages of Third-generation languages
▪ Greater readability: 3rd generation languages are more readable and easier to understand than 1GLs or 2GLs, which means that they are easier to write, debug, and maintain.
▪ Higher level of abstraction: These are more abstract and less bound to specific hardware architectures, meaning that programs written in third-generation languages can be more portable and easier to maintain.
▪ Greater support of software engineering principles: More adept at using software engineering principles, such as modular design and structured programming, which can lead to more maintainable and reliable code.
▪ Better support for large-scale development: More suitable for large-scale development projects, as they provide more powerful tools and abstractions for managing complexity.
▪ Improved productivity: Because they are easier to read and write, programmers can be more productive when using them.
▪ Better error handling: It has built-in error handling and debugging features, which can make it easier to identify and fix problems in a program.
Disadvantages third-generation languages (3GLs)
▪ Less control over the hardware: Not suitable for hardware-specific tasks because they do not provide as much control over the hardware as low-level languages.
▪ Slower execution speed: 3GL is usually compiled into machine code before execution, which can result in slower execution speed than programs written in low-level languages.
▪ Dependence on the compiler: Programs written in 3GL are usually compiled into machine code by a compiler, meaning they are dependent on the performance of the compiler to run correctly.
▪ Larger program size: 3GL programs can be larger than programs written in low-level languages, which can make them more difficult to store and transfer.
Fourth-generation (4G) languages
▪ These are specialized languages that are used to access databases.
▪ It is also called a non – procedural language or 4GL.
▪ Examples of Fourth-generation languages: SQL (Structured Query Language), Python, Perl, Ruby, and MatLab (matrix laboratory).
Also, Read: List of Computer Abbreviations (Updated)
Advantages of Fourth-generation languages
▪ Ease of use: It requires less coding and less technical knowledge than other general-purpose programming languages. This makes them accessible to a wide range of people, including non-developers.
▪ Increased productivity: Coding takes some time to learn, but 4th generation languages can help increase productivity due to less coding required.
▪ Better readability: These are more readable and easier to understand than general-purpose programming languages, which can make code easier to maintain and modify.
▪ Specificity: Since they are designed for a specific purpose, they may be more efficient and better suited to solving certain problems than general-purpose programming languages.
Disadvantages of Fourth-generation languages
▪ Limited scope: They are designed for specific purposes, so they may not be suitable for other types of troubleshooting or performing other tasks.
▪ Dependency on vendor support: Some of the 4th generation languages are developed and maintained by a specific vendor. This means that you may have to rely on the vendor for updates, support, and documentation.
▪ Lack of flexibility: They are not as flexible as a general-purpose programming language to perform a wide range of tasks and customize solutions.
▪ Poor performance: They are not suitable or efficient for performing tasks that require a lot of processing power or speed.
▪ Limited portability: Running solutions on different platforms and devices is difficult because they are often tied to a specific platform or operating system, which can make them difficult to port to other environments.
Fifth-generation (5G) languages
▪ The fifth-generation languages are also called 5GL.
▪ It is based on the concept of artificial intelligence (AI) and natural language processing (NLP).
▪ Parallel processing and superconductors are used for such languages to create real artificial intelligence.
▪ They are more human-like in their ability to process and understand information.
▪ Examples of Fifth-generation languages: PROLOG, LISP, OPS5, and Mercury
Advantages of Fifth-generation languages
▪ Increased productivity: Easier to learn and use than traditional programming languages, which can boost productivity. of a developer.
▪ Better readability: They are often designed with readability in mind, making the code easier to understand and maintain.
▪ Improved reliability: The machine can make decisions and find any errors in coding.
▪ Greater flexibility: They can be used to solve a wider range of problems.
Disadvantages Fifth-generation languages
▪ Limited scope: These are designed to solve specific types of problems like R&D in artificial intelligence.
▪ Lack of control: Fifth-generation languages are designed to solve given problems without a computer programmer. Thus the developer may have less control over the details of how their code is executed.
▪ Limited availability of developers: Fifth-generation languages such as OPS5 and Mercury are still not well known to developers, as they are specialized programming languages that are not as widely used as traditional programming languages such as C++ or Python.
Computer Languages Types and Generations Chart
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Answer: Machine language, Assembly language, and High-level language.
Answer: There are more than 500+ types of computer programming languages.
Answer: There are 5 generations of computer languages.
Answer: Third-generation languages.
Answer: SQL or Structured Query Language is included in the 4th generation languages.
Answer: 1960
• The first significantly expanded high-level language was Fortran
More Related Topics of Computer GK
Generation of computer 1st to 5th pdf
Top 10 Search Engines in 2022 with additional info
Computer Output and Input devices with examples
Types of Computers PDF
Storage Devices of Computer, Definitions, Types, and Examples
CD-ROM full form in Computer
▪ Hard to find errors Since programs are written in a binary code consisting of 0’s and 1’s, it makes it difficult to find an error in their written code.
▪ Lack of portability: They are tied to specific hardware architectures and cannot be easily ported to other platforms without rewriting.
▪ Portable: Programs written in 2GLs can often run on a wide variety of computers and operating systems without requiring significant modifications, making them more portable than programs written in first-generation languages.
▪ More flexible: Provide a wide range of features and programming constructs, such as loops, arrays, and functions, which make writing complex programs easy.
▪ Easier to learn: Second-generation languages use more familiar, English-like syntax and are generally easier to read and understand than first-generation languages.
▪ More efficient: They are compiled or interpreted into machine code, making them more efficient to run than programs written in first-generation languages.
Disadvantages of Second-generation languages
▪ Slower than first-generation languages: 2GLs can sometimes be slower than programs written in 1GLs because 2GLs are compiled or interpreted into machine code while 1st-generation languages are executed directly by the computer’s hardware.
▪ More memory required: It requires more memory to run than those written in first-generation languages, as they may include additional instructions for the compiler or interpreter to execute.
▪ More complex than 1st Generation language: Second-generation languages offer a wider range of features and programming structures, which can make them more complex to learn and use.
Third-generation (3G) languages
▪ Third-generation or 3GL languages are high-level procedural languages and are more abstract and closer to human language.
▪ They are easier to write, read and maintain than 1G and 2G languages because the written instructions consist of a series of words like English.
▪ Examples of third-generation languages: C, C++, PASCAL, FORTRAN, COBOL, Visual Basic, and Java.
Advantages of Third-generation languages
▪ Greater readability: 3rd generation languages are more readable and easier to understand than 1GLs or 2GLs, which means that they are easier to write, debug, and maintain.
▪ Higher level of abstraction: These are more abstract and less bound to specific hardware architectures, meaning that programs written in third-generation languages can be more portable and easier to maintain.
▪ Greater support of software engineering principles: More adept at using software engineering principles, such as modular design and structured programming, which can lead to more maintainable and reliable code.
▪ Better support for large-scale development: More suitable for large-scale development projects, as they provide more powerful tools and abstractions for managing complexity.
▪ Improved productivity: Because they are easier to read and write, programmers can be more productive when using them.
▪ Better error handling: It has built-in error handling and debugging features, which can make it easier to identify and fix problems in a program.
Disadvantages third-generation languages (3GLs)
▪ Less control over the hardware: Not suitable for hardware-specific tasks because they do not provide as much control over the hardware as low-level languages.
▪ Slower execution speed: 3GL is usually compiled into machine code before execution, which can result in slower execution speed than programs written in low-level languages.
▪ Dependence on the compiler: Programs written in 3GL are usually compiled into machine code by a compiler, meaning they are dependent on the performance of the compiler to run correctly.
▪ Larger program size: 3GL programs can be larger than programs written in low-level languages, which can make them more difficult to store and transfer.
Fourth-generation (4G) languages
▪ These are specialized languages that are used to access databases.
▪ It is also called a non – procedural language or 4GL.
▪ Examples of Fourth-generation languages: SQL (Structured Query Language), Python, Perl, Ruby, and MatLab (matrix laboratory).
Also, Read: List of Computer Abbreviations (Updated)
Advantages of Fourth-generation languages
▪ Ease of use: It requires less coding and less technical knowledge than other general-purpose programming languages. This makes them accessible to a wide range of people, including non-developers.
▪ Increased productivity: Coding takes some time to learn, but 4th generation languages can help increase productivity due to less coding required.
▪ Better readability: These are more readable and easier to understand than general-purpose programming languages, which can make code easier to maintain and modify.
▪ Specificity: Since they are designed for a specific purpose, they may be more efficient and better suited to solving certain problems than general-purpose programming languages.
Disadvantages of Fourth-generation languages
▪ Limited scope: They are designed for specific purposes, so they may not be suitable for other types of troubleshooting or performing other tasks.
▪ Dependency on vendor support: Some of the 4th generation languages are developed and maintained by a specific vendor. This means that you may have to rely on the vendor for updates, support, and documentation.
▪ Lack of flexibility: They are not as flexible as a general-purpose programming language to perform a wide range of tasks and customize solutions.
▪ Poor performance: They are not suitable or efficient for performing tasks that require a lot of processing power or speed.
▪ Limited portability: Running solutions on different platforms and devices is difficult because they are often tied to a specific platform or operating system, which can make them difficult to port to other environments.
Fifth-generation (5G) languages
▪ The fifth-generation languages are also called 5GL.
▪ It is based on the concept of artificial intelligence (AI) and natural language processing (NLP).
▪ Parallel processing and superconductors are used for such languages to create real artificial intelligence.
▪ They are more human-like in their ability to process and understand information.
▪ Examples of Fifth-generation languages: PROLOG, LISP, OPS5, and Mercury
Advantages of Fifth-generation languages
▪ Increased productivity: Easier to learn and use than traditional programming languages, which can boost productivity. of a developer.
▪ Better readability: They are often designed with readability in mind, making the code easier to understand and maintain.
▪ Improved reliability: The machine can make decisions and find any errors in coding.
▪ Greater flexibility: They can be used to solve a wider range of problems.
Disadvantages Fifth-generation languages
▪ Limited scope: These are designed to solve specific types of problems like R&D in artificial intelligence.
▪ Lack of control: Fifth-generation languages are designed to solve given problems without a computer programmer. Thus the developer may have less control over the details of how their code is executed.
▪ Limited availability of developers: Fifth-generation languages such as OPS5 and Mercury are still not well known to developers, as they are specialized programming languages that are not as widely used as traditional programming languages such as C++ or Python.
Computer Languages Types and Generations Chart

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Answer: Machine language, Assembly language, and High-level language.
Answer: There are more than 500+ types of computer programming languages.
Answer: There are 5 generations of computer languages.
Answer: Third-generation languages.
Answer: SQL or Structured Query Language is included in the 4th generation languages.
Answer: 1960
• The first significantly expanded high-level language was Fortran
More Related Topics of Computer GK
Generation of computer 1st to 5th pdf
Top 10 Search Engines in 2022 with additional info
Computer Output and Input devices with examples
Types of Computers PDF
Storage Devices of Computer, Definitions, Types, and Examples
CD-ROM full form in Computer
▪ Portable: Programs written in 2GLs can often run on a wide variety of computers and operating systems without requiring significant modifications, making them more portable than programs written in first-generation languages.
▪ More flexible: Provide a wide range of features and programming constructs, such as loops, arrays, and functions, which make writing complex programs easy.
▪ Easier to learn: Second-generation languages use more familiar, English-like syntax and are generally easier to read and understand than first-generation languages.
▪ More efficient: They are compiled or interpreted into machine code, making them more efficient to run than programs written in first-generation languages.
Disadvantages of Second-generation languages
▪ Slower than first-generation languages: 2GLs can sometimes be slower than programs written in 1GLs because 2GLs are compiled or interpreted into machine code while 1st-generation languages are executed directly by the computer’s hardware.
▪ More memory required: It requires more memory to run than those written in first-generation languages, as they may include additional instructions for the compiler or interpreter to execute.
▪ Greater readability: 3rd generation languages are more readable and easier to understand than 1GLs or 2GLs, which means that they are easier to write, debug, and maintain.
▪ Higher level of abstraction: These are more abstract and less bound to specific hardware architectures, meaning that programs written in third-generation languages can be more portable and easier to maintain.
▪ Greater support of software engineering principles: More adept at using software engineering principles, such as modular design and structured programming, which can lead to more maintainable and reliable code.
▪ Better support for large-scale development: More suitable for large-scale development projects, as they provide more powerful tools and abstractions for managing complexity.
▪ Improved productivity: Because they are easier to read and write, programmers can be more productive when using them.
▪ Better error handling: It has built-in error handling and debugging features, which can make it easier to identify and fix problems in a program.
Disadvantages third-generation languages (3GLs)
▪ Less control over the hardware: Not suitable for hardware-specific tasks because they do not provide as much control over the hardware as low-level languages.
▪ Slower execution speed: 3GL is usually compiled into machine code before execution, which can result in slower execution speed than programs written in low-level languages.
▪ Dependence on the compiler: Programs written in 3GL are usually compiled into machine code by a compiler, meaning they are dependent on the performance of the compiler to run correctly.
▪ Larger program size: 3GL programs can be larger than programs written in low-level languages, which can make them more difficult to store and transfer.
Fourth-generation (4G) languages
▪ These are specialized languages that are used to access databases.
▪ It is also called a non – procedural language or 4GL.
▪ Examples of Fourth-generation languages: SQL (Structured Query Language), Python, Perl, Ruby, and MatLab (matrix laboratory).
Also, Read: List of Computer Abbreviations (Updated)
Advantages of Fourth-generation languages
▪ Ease of use: It requires less coding and less technical knowledge than other general-purpose programming languages. This makes them accessible to a wide range of people, including non-developers.
▪ Increased productivity: Coding takes some time to learn, but 4th generation languages can help increase productivity due to less coding required.
▪ Better readability: These are more readable and easier to understand than general-purpose programming languages, which can make code easier to maintain and modify.
▪ Specificity: Since they are designed for a specific purpose, they may be more efficient and better suited to solving certain problems than general-purpose programming languages.
Disadvantages of Fourth-generation languages
▪ Limited scope: They are designed for specific purposes, so they may not be suitable for other types of troubleshooting or performing other tasks.
▪ Dependency on vendor support: Some of the 4th generation languages are developed and maintained by a specific vendor. This means that you may have to rely on the vendor for updates, support, and documentation.
▪ Lack of flexibility: They are not as flexible as a general-purpose programming language to perform a wide range of tasks and customize solutions.
▪ Poor performance: They are not suitable or efficient for performing tasks that require a lot of processing power or speed.
▪ Limited portability: Running solutions on different platforms and devices is difficult because they are often tied to a specific platform or operating system, which can make them difficult to port to other environments.
Fifth-generation (5G) languages
▪ The fifth-generation languages are also called 5GL.
▪ It is based on the concept of artificial intelligence (AI) and natural language processing (NLP).
▪ Parallel processing and superconductors are used for such languages to create real artificial intelligence.
▪ They are more human-like in their ability to process and understand information.
▪ Examples of Fifth-generation languages: PROLOG, LISP, OPS5, and Mercury
Advantages of Fifth-generation languages
▪ Increased productivity: Easier to learn and use than traditional programming languages, which can boost productivity. of a developer.
▪ Better readability: They are often designed with readability in mind, making the code easier to understand and maintain.
▪ Improved reliability: The machine can make decisions and find any errors in coding.
▪ Greater flexibility: They can be used to solve a wider range of problems.
Disadvantages Fifth-generation languages
▪ Limited scope: These are designed to solve specific types of problems like R&D in artificial intelligence.
▪ Lack of control: Fifth-generation languages are designed to solve given problems without a computer programmer. Thus the developer may have less control over the details of how their code is executed.
▪ Limited availability of developers: Fifth-generation languages such as OPS5 and Mercury are still not well known to developers, as they are specialized programming languages that are not as widely used as traditional programming languages such as C++ or Python.
Computer Languages Types and Generations Chart

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Answer: Machine language, Assembly language, and High-level language.
Answer: There are more than 500+ types of computer programming languages.
Answer: There are 5 generations of computer languages.
Answer: Third-generation languages.
Answer: SQL or Structured Query Language is included in the 4th generation languages.
Answer: 1960
• The first significantly expanded high-level language was Fortran
More Related Topics of Computer GK
Generation of computer 1st to 5th pdf
Top 10 Search Engines in 2022 with additional info
Computer Output and Input devices with examples
Types of Computers PDF
Storage Devices of Computer, Definitions, Types, and Examples
CD-ROM full form in Computer
▪ Greater readability: 3rd generation languages are more readable and easier to understand than 1GLs or 2GLs, which means that they are easier to write, debug, and maintain.
▪ Higher level of abstraction: These are more abstract and less bound to specific hardware architectures, meaning that programs written in third-generation languages can be more portable and easier to maintain.
▪ Greater support of software engineering principles: More adept at using software engineering principles, such as modular design and structured programming, which can lead to more maintainable and reliable code.
▪ Ease of use: It requires less coding and less technical knowledge than other general-purpose programming languages. This makes them accessible to a wide range of people, including non-developers.
▪ Increased productivity: Coding takes some time to learn, but 4th generation languages can help increase productivity due to less coding required.
▪ Better readability: These are more readable and easier to understand than general-purpose programming languages, which can make code easier to maintain and modify.
▪ Specificity: Since they are designed for a specific purpose, they may be more efficient and better suited to solving certain problems than general-purpose programming languages.
Disadvantages of Fourth-generation languages
▪ Limited scope: They are designed for specific purposes, so they may not be suitable for other types of troubleshooting or performing other tasks.
▪ Dependency on vendor support: Some of the 4th generation languages are developed and maintained by a specific vendor. This means that you may have to rely on the vendor for updates, support, and documentation.
▪ Lack of flexibility: They are not as flexible as a general-purpose programming language to perform a wide range of tasks and customize solutions.
▪ Poor performance: They are not suitable or efficient for performing tasks that require a lot of processing power or speed.
▪ Limited portability: Running solutions on different platforms and devices is difficult because they are often tied to a specific platform or operating system, which can make them difficult to port to other environments.
Fifth-generation (5G) languages
▪ The fifth-generation languages are also called 5GL.
▪ It is based on the concept of artificial intelligence (AI) and natural language processing (NLP).
▪ Parallel processing and superconductors are used for such languages to create real artificial intelligence.
▪ They are more human-like in their ability to process and understand information.
▪ Examples of Fifth-generation languages: PROLOG, LISP, OPS5, and Mercury
Advantages of Fifth-generation languages
▪ Increased productivity: Easier to learn and use than traditional programming languages, which can boost productivity. of a developer.
▪ Better readability: They are often designed with readability in mind, making the code easier to understand and maintain.
▪ Improved reliability: The machine can make decisions and find any errors in coding.
▪ Greater flexibility: They can be used to solve a wider range of problems.
Disadvantages Fifth-generation languages
▪ Limited scope: These are designed to solve specific types of problems like R&D in artificial intelligence.
▪ Lack of control: Fifth-generation languages are designed to solve given problems without a computer programmer. Thus the developer may have less control over the details of how their code is executed.
▪ Limited availability of developers: Fifth-generation languages such as OPS5 and Mercury are still not well known to developers, as they are specialized programming languages that are not as widely used as traditional programming languages such as C++ or Python.
Computer Languages Types and Generations Chart

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Answer: Machine language, Assembly language, and High-level language.
Answer: There are more than 500+ types of computer programming languages.
Answer: There are 5 generations of computer languages.
Answer: Third-generation languages.
Answer: SQL or Structured Query Language is included in the 4th generation languages.
Answer: 1960
• The first significantly expanded high-level language was Fortran
More Related Topics of Computer GK
Generation of computer 1st to 5th pdf
Top 10 Search Engines in 2022 with additional info
Computer Output and Input devices with examples
Types of Computers PDF
Storage Devices of Computer, Definitions, Types, and Examples
CD-ROM full form in Computer
▪ Ease of use: It requires less coding and less technical knowledge than other general-purpose programming languages. This makes them accessible to a wide range of people, including non-developers.
▪ Increased productivity: Coding takes some time to learn, but 4th generation languages can help increase productivity due to less coding required.
▪ Better readability: These are more readable and easier to understand than general-purpose programming languages, which can make code easier to maintain and modify.
▪ Specificity: Since they are designed for a specific purpose, they may be more efficient and better suited to solving certain problems than general-purpose programming languages.
Disadvantages of Fourth-generation languages
▪ Limited scope: They are designed for specific purposes, so they may not be suitable for other types of troubleshooting or performing other tasks.
▪ Poor performance: They are not suitable or efficient for performing tasks that require a lot of processing power or speed.
▪ Limited portability: Running solutions on different platforms and devices is difficult because they are often tied to a specific platform or operating system, which can make them difficult to port to other environments.
Fifth-generation (5G) languages
▪ The fifth-generation languages are also called 5GL.
▪ It is based on the concept of artificial intelligence (AI) and natural language processing (NLP).
▪ Parallel processing and superconductors are used for such languages to create real artificial intelligence.
▪ They are more human-like in their ability to process and understand information.
▪ Examples of Fifth-generation languages: PROLOG, LISP, OPS5, and Mercury
Advantages of Fifth-generation languages
▪ Increased productivity: Easier to learn and use than traditional programming languages, which can boost productivity. of a developer.
▪ Better readability: They are often designed with readability in mind, making the code easier to understand and maintain.
▪ Improved reliability: The machine can make decisions and find any errors in coding.
▪ Greater flexibility: They can be used to solve a wider range of problems.
Disadvantages Fifth-generation languages
▪ Limited scope: These are designed to solve specific types of problems like R&D in artificial intelligence.
▪ Lack of control: Fifth-generation languages are designed to solve given problems without a computer programmer. Thus the developer may have less control over the details of how their code is executed.
▪ Limited availability of developers: Fifth-generation languages such as OPS5 and Mercury are still not well known to developers, as they are specialized programming languages that are not as widely used as traditional programming languages such as C++ or Python.
Computer Languages Types and Generations Chart

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Answer: Machine language, Assembly language, and High-level language.
Answer: There are more than 500+ types of computer programming languages.
Answer: There are 5 generations of computer languages.
Answer: Third-generation languages.
Answer: SQL or Structured Query Language is included in the 4th generation languages.
Answer: 1960
• The first significantly expanded high-level language was Fortran
More Related Topics of Computer GK
Generation of computer 1st to 5th pdf
Top 10 Search Engines in 2022 with additional info
Computer Output and Input devices with examples
Types of Computers PDF
Storage Devices of Computer, Definitions, Types, and Examples
CD-ROM full form in Computer
▪ Poor performance: They are not suitable or efficient for performing tasks that require a lot of processing power or speed.
▪ Limited portability: Running solutions on different platforms and devices is difficult because they are often tied to a specific platform or operating system, which can make them difficult to port to other environments.
▪ The fifth-generation languages are also called 5GL.
▪ It is based on the concept of artificial intelligence (AI) and natural language processing (NLP).
▪ Parallel processing and superconductors are used for such languages to create real artificial intelligence.
▪ They are more human-like in their ability to process and understand information.
▪ Limited scope: These are designed to solve specific types of problems like R&D in artificial intelligence.
▪ Lack of control: Fifth-generation languages are designed to solve given problems without a computer programmer. Thus the developer may have less control over the details of how their code is executed.
▪ Limited availability of developers: Fifth-generation languages such as OPS5 and Mercury are still not well known to developers, as they are specialized programming languages that are not as widely used as traditional programming languages such as C++ or Python.
Computer Languages Types and Generations Chart

Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Answer: Machine language, Assembly language, and High-level language.
Answer: There are more than 500+ types of computer programming languages.
Answer: There are 5 generations of computer languages.
Answer: Third-generation languages.
Answer: SQL or Structured Query Language is included in the 4th generation languages.
Answer: 1960
• The first significantly expanded high-level language was Fortran
More Related Topics of Computer GK
Generation of computer 1st to 5th pdf
Top 10 Search Engines in 2022 with additional info
Computer Output and Input devices with examples
Types of Computers PDF
Storage Devices of Computer, Definitions, Types, and Examples
CD-ROM full form in Computer
▪ Limited scope: These are designed to solve specific types of problems like R&D in artificial intelligence.
source
—
Note that any programming tips and code writing requires some knowledge of computer programming. Please, be careful if you do not know what you are doing…